As cryptocurrency gains even more popularity and adoption in today's society, scammers are infiltrating the industry. As a result, all crypto investors must remain vigilant and proactive.
Email scams
Email scams are among the most popular crypto scams, with the thief initially attempting to attract the receiver's attention in order to entice the user into the scam. The next step is typically to advise an action to be taken, such as to 'cancel a transaction' or 'connect/login to a wallet address'; this is usually done by providing a link or button to click. These emails are referred to as 'phishing emails.' The same method can be used to carry out scams on social media, messaging platforms (Discord, Telegram), counterfeit apps, giveaways, false websites, or fake investment opportunities.

Scammers frequently pose as trustworthy personalities, such as wealthy investors, influencers (celebrities), or members of recognised platforms' support teams. It is crucial to remember that exchanges and other hot wallet providers will never request your login information or request that you transfer funds for verification or other purposes. It is critical for the safety of one's funds to never click links that appear inauthentic or are 'fishing' for information, as visiting the link alone can install malware on your system or allow the fraudster access to your personal details. A simple rule that can assist detect possible scams, particularly those that offer monetary rewards for participation, is that if anything appears too good to be true, it probably is.
While the most prevalent frauds are variations on the above-described technique, crypto scammers are seeking to acquire access to cash using practically every medium available. More examples of tactics fraudsters may use to try to deceive you into allowing them to steal your funds are provided below:
Fraudulent Tactics Used by Scammers
Free Airdrops
- Counterfeit airdrops may ask you for certain wallet information such as your private keys or seed phrase in order to receive the airdrop. You may also be asked to donate money in order to be eligible for the airdrop. Genuine airdrops should never ask for this information because all that is needed for a successful airdrop is the wallet's public address that is captured via a snapshot. More recently, individuals are required to connect their wallet and sign a transaction to be eligible to “claim” the free tokens through their wallet.
Further reading: What is a crypto airdrop?
Imposters
-
Scammers often contact people while impersonating a trusted company or individual. Major crypto businesses often have imposters pretending to represent the company who may ask investors to send them coins or open suspicious links. It is important to always check who is contacting you, making sure the email address and URL are both accurate. If you are ever uncertain, you should always be cautious and reach out to the company or exchange directly to confirm. Never open suspicious links or send coins without double checking the contact information for the person contacting you.
-
For example, at Caleb & Brown, your broker will never ask for your private keys and so any communication appearing to be from Caleb & Brown with this request is a scam. If you are ever unsure if communication you receive is legitimate, you can always contact your broker via their mobile phone number provided to you originally or through Caleb & Brown’s official website to check the communication you have received is authentic.
Deals
- You may receive offers or promotions for purchasing tokens. Whether they are bulk deals in which you receive a discount for purchasing a large amount or any offer in which you are given the opportunity to acquire tokens/NFTs at a cheaper price than the market. Any offer in any form of this is almost certainly a scam and it is never worth the risk.
Private Keys
- As previously mentioned, you should keep your private key and seed phrase in the safest manner possible, such as by writing them down on different pieces of paper. Never share your private keys or seed phrases and never save them anywhere online. Scammers may call you and ask for private keys or seed phrase in order to transfer you money or with the ‘promise’ of some other type of reward. To be clear, you should never disclose your private keys or seed phrases with anybody.
Earn Rewards on Tokens
- Scammers may approach you and invite you to participate in a 'rewards scheme,' in which they guarantee you huge profits/gains on the tokens you submit to them. To make the fraud appear more legitimate, they will either ask you to deposit your tokens into their wallet or offer you a non-authentic website link. The two most prevalent ways to do this are to submit your tokens with the promise of these benefits through a staking program/platform or by mining for incentives. In any of these fraudulent scenarios, your tokens were most likely not staked or used for mining power but were instead directed to the scammer's wallet.
Too Good to be True Offers
- Another popular scam to be wary of is one in which the contact states, "If you send me 10 tokens, I will pay you 20 back!" Scammers frequently use time pressure, such as 'just 30 minutes left!' to induce an element of FOMO and pressure the receiver into continuing with the fraud without having time to conduct their own due diligence. If you are ever offered a deal that proposes to send you more tokens back than you send to them, it is always a fraud, no matter how credible this offer appears to be. This is a prime example of when an offer appears too good to be true, it is!
Some examples of aforementioned scams can be seen below (images reproduced in line with fair dealing exceptions in the Copyright Act 1968 (Cth)):
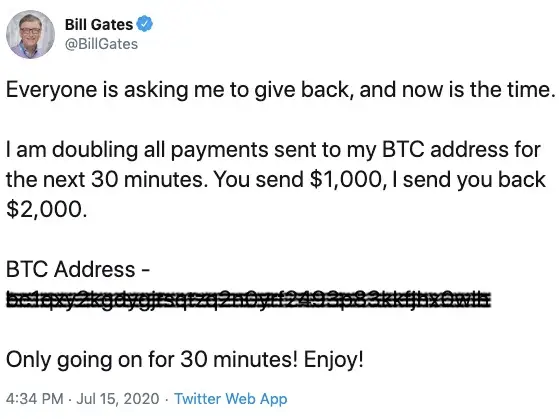
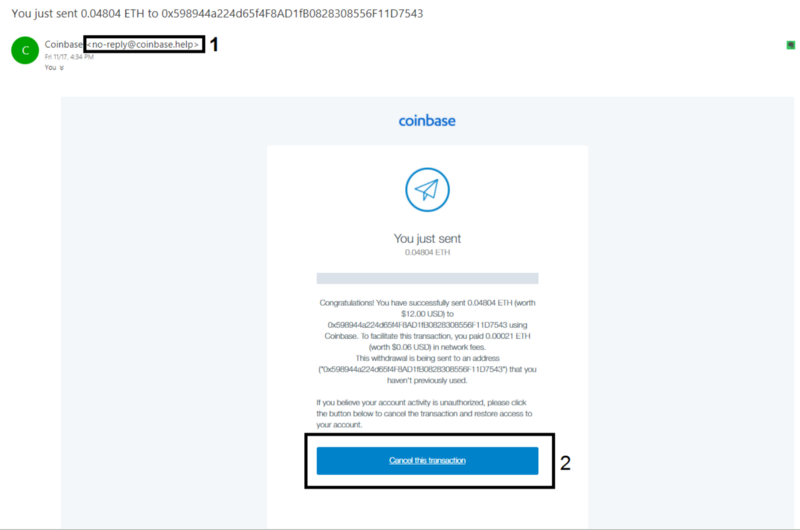

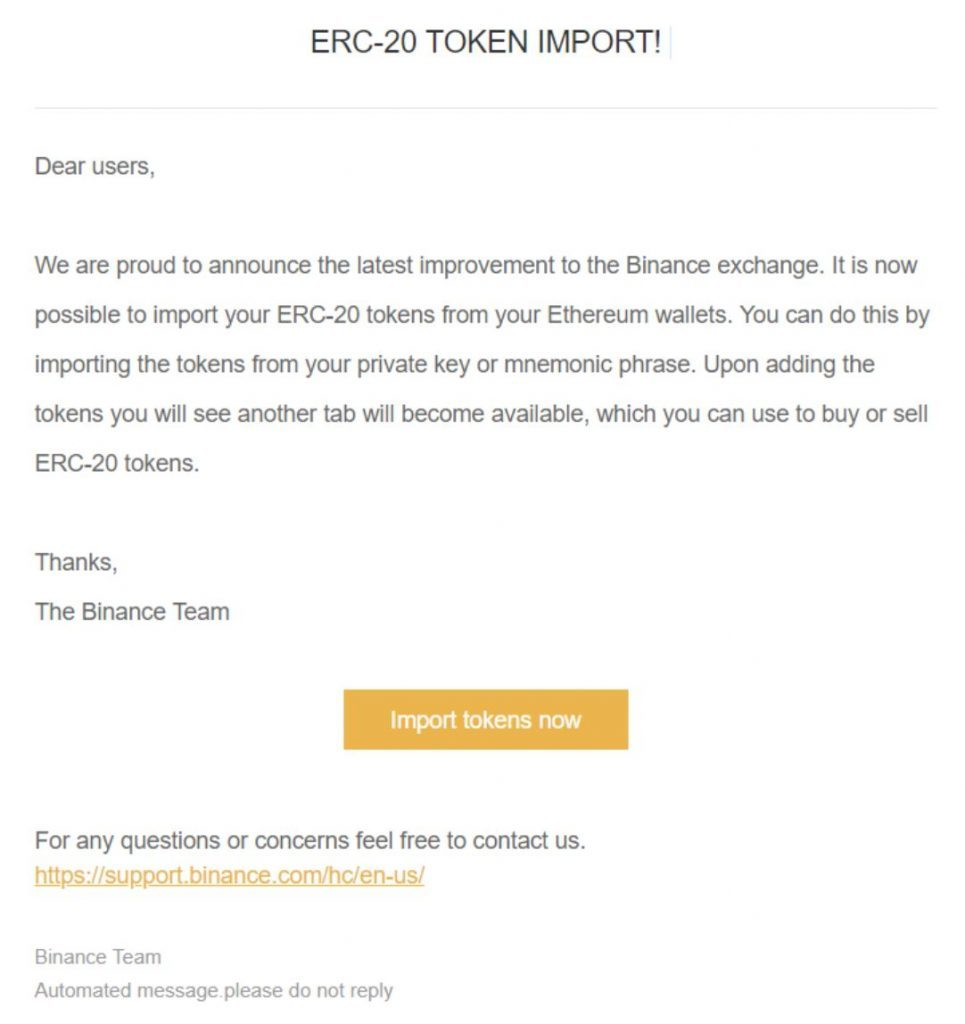
If you are ever in doubt or suspect a scam, please do not hesitate to contact your Caleb & Brown broker for a second perspective. They will gladly assist you in confirming the validity of any communications you may get in order to avoid falling victim to fraudulent activities and to keep your assets safe and secure.
Caleb & Brown offers enhanced security and due diligence protocols as well as industry-leading cold storage solutions. If you're not already a Caleb & Brown client but would like to be, sign up today for your free security consultation.
Catch up on part 1 of our Crypto Security 101 series: Best Practices
Disclaimer: This assessment does not consider your personal circumstances, and should not be construed as financial, legal or investment advice. These thoughts are ours only and should only be taken as educational by the reader. Under no circumstances do we make recommendation or assurance towards the views expressed in the blog-post. The Company disclaims all duties and liabilities, including liability for negligence, for any loss or damage which is suffered or incurred by any person acting on any information provided.
from Caleb & Brown Cryptocurrency Brokerage.

.png?u=https%3A%2F%2Fimages.ctfassets.net%2F4ua9vnmkuhzj%2F4jYgHrC8XOFlsARFkIAlWK%2F18c3fc3c2948bf035a87801c342b252a%2FWeekly_Rollup_Blog_Tiles_3840x2160_staying_safe__1_.png&a=w%3D480%26h%3D270%26fm%3Dpng%26q%3D80&cd=2024-11-26T05%3A20%3A42.745Z)




