On September 15, 2022, Ethereum’s long-awaited Merge was executed, marking the network’s transition from a Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. As this content was written pre-Merge, any mentions of Ethereum using PoW are in reference to the network’s previous consensus mechanism, not its current one.
The Merge is upon us.
The most significant update in the history of Ethereum (and potentially the entire crypto space) will see the chain switch to a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. After years of testing, development, and countless delays, the process is now in its final stages and is expected to take place mid-September 2022. This article covers everything you need to know about The Merge and how it will change the future of Ethereum.
What is The Merge?
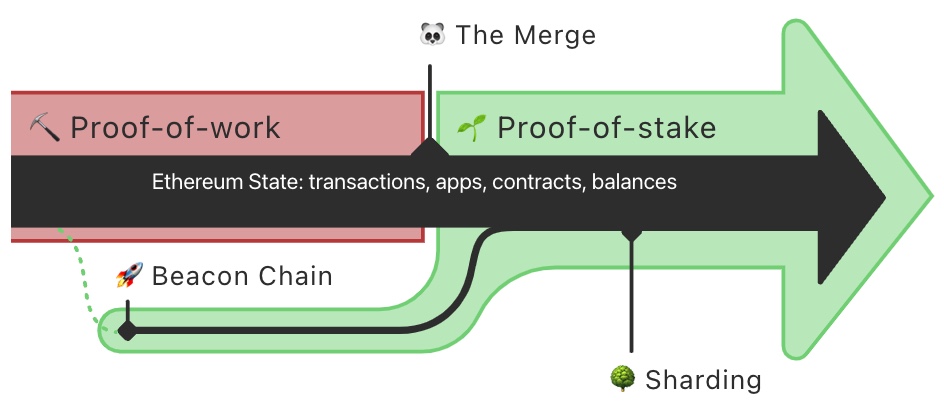
‘The Merge’ is the name of the event where the Ethereum blockchain will change its consensus mechanism from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS). It’s known as ‘The Merge’ because it will involve the merging of the main Ethereum blockchain with a special purpose blockchain called ‘the Beacon Chain’.
The Beacon Chain launched December 2020 with the sole purpose of one thing and one thing only: to be a PoS blockchain for Ethereum. For the past 20 months, the Beacon Chain has been an empty blockchain, hosting no transactions, tokens, DeFi apps or NFTs. It has been running in parallel to the Ethereum Mainnet using PoS for developers to run tests and updates.
The approaching Merge is when these two systems finally come together, and PoW is replaced by a brand new PoS consensus mechanism. This event has been likened by Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin to hot-swapping the engine of a spaceship with a new engine mid-flight.
What’s the Difference Between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake?
PoS is an alternative consensus mechanism to PoW, used by blockchains like Solana, Cardano, and Avalanche. With PoW, miners prove they have capital at risk by expending energy to solve complex computational problems, while competing for the right to validate and create blocks.
In PoS, validators stake capital in the form of Ether (ETH) to participate in securing the network. This staked ETH then acts as collateral that can be destroyed if validators behave dishonestly or lazily. The risk of penalties discourages any misbehaviour.
Why Merge?
Since its genesis, PoW has secured the Ethereum Mainnet. This is the Ethereum blockchain we've all known and loved (when it’s not expensive to use). However, throughout Ethereum’s history, developers have been hard at work preparing for an eventual transition to PoS. But why?
Energy Efficiency
At its core, The Merge to PoS will reduce network energy usage by at least 99.95%. With the current PoW model, the Ethereum network has about the same carbon footprint as the entire nation of Finland. Moving to PoS eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining and instead secures the network using staked ETH.
Security
The threat of 51% attacks and other malicious activity still exists on both PoW and PoS, but the Ethereum developers believe PoS offers greater crypto-economic security than PoW.
The security model for PoS is based on stakers, who put up economic value (in the form of ETH). These participants are deterred from acting maliciously towards the network through the risk of losing or devaluing their staked capital. Economic penalties for misbehavior in the form of “slashing” make it more costly for bad actors to attempt attacks.
Decentralisation
Staking makes it easier for anyone to participate in securing the Ethereum network. It has much lower barriers to entry and reduced hardware requirements, as validator nodes can run on a normal laptop. This contrasts with PoW, where economies of scale make it difficult for small-scale miners to compete with larger mining farms. With PoS, staking pools also allow users to stake their ETH without needing to have 32 ETH.
With more users able to participate in securing the network, control is distributed across Ethereum and not concentrated among a few large players. This in theory should lead to more network decentralisation.
Future Scalability
As the number of people using Ethereum has grown, the blockchain has reached certain capacity limitations. This has driven up the cost of using the network, creating the need for scaling solutions. The existing PoW system would become increasingly difficult to scale long term as Ethereum continues to grow. A transition to PoS has become necessary to fulfil Ethereum’s rollup-centric roadmap and future plans for sharding.
How will The Merge Impact ETH?
While The Merge will completely reshape the Ethereum network, it will also have major consequences for ETH the asset. The Merge will drastically impact the economics of ETH in three major ways: reduction in ETH issuance, ETH burn mechanism, and ETH staking. For investors and traders alike, this change in ETH dynamics is likely the most significant aspect of The Merge.
The Triple Halvening
The Merge has been nicknamed ‘the triple halvening’ by some members of the Ethereum community because the supply shock to ETH will be equivalent to three Bitcoin halvings - an event that programmatically occurs roughly every 4 years where the supply issuance of Bitcoin per block is cut by 50%.
The reduction in ETH supply caused by The Merge would take Bitcoin 12 years (three block reward halvings) to do what Ethereum is going to do in the next 2 weeks.
1. Reduction in ETH Issuance
The Merge will reduce yearly ETH issuance by 90%, from 4.3% to 0.43%. This reduction is driven by the fundamental improvements a PoS consensus mechanism brings to Ethereum.
What does it improve? The current PoW system is expensive and requires significant overhead costs to compensate security providers (miners) for their services. As a result, the network needs to issue considerable amounts of currency (ETH) to pay for security. Ethereum currently issues around 13,500 ETH per day, with an annual issuance of approximately 4.3% of ETH’s total supply.
By contrast, PoS is designed to provide the highest level of security, for the lowest amount of cost, and these savings are passed into ETH. The cost of PoS security is only the opportunity cost of capital, which does not require any real-world or tangible expense. So, PoS does not need to issue the same amount of currency to pay for security, making it more efficient.
2. ETH Burn Mechanism
This time last year, Ethereum released an Improvement Proposal known as the London Hard Fork (or EIP-1559) which modified how transaction fees are handled on Ethereum. Rather than paying the entire transaction fees to the miners, a portion would be taken out of the circulating supply and burnt instead, in a way similar to a share buyback.
The burn mechanism is directly impacted by The Merge, with ETH’s issuance dropping by 90%, it will increase the proportional magnitude of how much ETH is burned every block. When gas fees on Ethereum are 7 gwei or higher, the rate of ETH being burnt will be higher than the rate of ETH being issued, causing the circulating supply of ETH to decrease*.* For context, during the peak of the 2021 bull market, gas prices remained at or above 200 gwei for several months, making that 7 gwei level a very low bar to clear.
Since August 2021, over 2.5 million ETH has been burned (and removed from the supply forever). If more ETH continues to be burned than issued, ETH becomes a deflationary asset. This would give ETH harder monetary properties that are closer to Gold or Bitcoin, and has seen it labelled as ‘ultra sound money’ by some Ethereum proponents.
3. ETH Staking
Post-Merge, the ETH staking rate is projected to increase by ~100 basis points from 4.2% to 5.2%. However, with the transition to PoS, stakers will now earn rewards in return for locking up their capital and helping secure the network. This transforms ETH into a productive asset since holders can generate a return from staking. With ETH as an interest-bearing asset, ETH holders are therefore incentivised to stake their ETH for yield. As more ETH is staked, the available supply on the market will be reduced.
The Merge event also introduces an interesting supply dynamic for the next six months. Stakers will be unable to withdraw any of their staked ETH until the next Shanghai upgrade at least six months after The Merge. This makes all the staked ETH to date (around 13.2 million ETH) and any newly issued ETH after The Merge illiquid and essentially off the market. After the initial six-month period, a queue will allow for gradual withdrawal that will effectively reduce the circulating supply temporarily.
This may also have knock on effects on the sell pressure felt by ETH miners. In the existing PoW system, miners are usually forced sellers of their ETH rewards due to the business model’s narrow profit margins. With PoS, the overhead costs of being a PoS validator basically falls to zero, so there is reduced selling pressure. The incentive for miners is no longer to dump rewards, but to restake to earn more rewards.
Top 5 Misconceptions about The Merge
With The Merge attracting so much media attention and speculation, there are plenty of misconceptions spreading across the crypto community. Here are five of the most common.
The Merge will Reduce Gas Fees
This claim is, in short, inaccurate. However, The Merge could lead to decreased gas fees in the future. The Merge is a change of consensus mechanism, not an expansion of network capacity, and will not result in lower gas fees. This misconception stems largely from confusion between ‘The Merge ‘and what was known as ‘Ethereum 2.0’.
However, the move to PoS sets the stage for Ethereum’s rollup-centric roadmap and sharding which will make gas fees exponentially cheaper in the future.
Transaction Speed will Increase Greatly
Though there will be some slights changes, transaction speed will mostly remain the same.
After The Merge, Ethereum’s block time will be marginally faster, from an average block time of 13.6 seconds to 12 seconds. This is a 12% increase in transaction capacity and thus a 12% reduction in gas cost. But this is considered a negligible amount that won’t make a material difference and so isn’t considered a lowering of gas fees.
All Staked ETH will be Withdrawn after The Merge
Staking withdrawals are not enabled with The Merge. Withdrawals will be introduced with the Shanghai upgrade, the next major Ethereum upgrade, which is expected to take place 6-12 months after The Merge. This is done for security reasons. Even when they are introduced, there are limitations set in place to limit the number of ETH that can be withdrawn each day.
The Merge will Result in Network Downtime
The Merge upgrade is designed to transition to PoS with zero downtime to disrupt the network or its users. The network should keep functioning as intended at all times.
Running a Node Requires 32 ETH
Anyone is free to run a node. No ETH is required. Not before or after The Merge.
There are two types of nodes on the Ethereum network – ones that can propose blocks and ones that can’t. Those that are not required to commit ETH do not propose blocks but they are also integral to the network’s security because they hold all block proposers accountable.
Top 5 FAQs about The Merge
When is The Merge?
Ethereum’s final testnet Merge successfully took place on the Goerli Network on August 10. With this final test completed, The Merge has officially been scheduled for Ethereum’s mainnet. The Merge will be triggered at a Terminal Total Difficulty (TTD) of 58750000000000000000000. TTD is expected to be reached around September 15, 2022, around 12:00 UTC. However, this may vary depending on the variable hash rate, and the Ethereum Foundation has indicated the merge could occur any time between September 10-20, 2022.
Is The Merge Priced in?
The question on every investor and traders mind. And the hardest one to answer.
This is the most significant event of its kind. It comes at a time where crypto faces a bear market and is searching for a narrative to bolster the market. This psychological question is one best answered retrospectively than trying to predict the future. We'll be closely following The Merge and the price of ETH as it unfolds.
Is The Merge Risky?
It’s fair to say, there’s a lot at stake.
The Merge is considered one of the biggest events in crypto history because no blockchain has undergone such a significant change before. This brings with it a significant amount of technical challenges and risks of getting something wrong. But this is also why The Merge has taken so long and been delayed so often, as the Ethereum team has been thoroughly testing it for years to ensure they deliver.
Will there be a Fork of the New Ethereum Chain?
Potentially. Some miners are reportedly working to hard fork the chain - that is, to split the chain into a separate network that will continue using the PoW consensus mechanism. This would not be the first time Ethereum has undergone a hard fork; the most famous of which was the Ethereum Classic split in 2016.
Do I Need to do Anything to My ETH?
No. If you are using ETH on-chain or holding ETH, you don’t need to perform any actions during or after The Merge. As the upgrade is based on the protocol, there will be no direct impact on the users or holders.
If an application, exchange, or wallet you use offers additional instructions or recommendations, you should verify these are actually coming from them. Be on the lookout for scams!
The Merge Countdown is On
Ethereum is about to undergo the most significant upgrade in its history, which will completely reshape the blockchain as we know it. The Merge to PoS is seen as the only viable way of realising Ethereum’s vision of a highly sustainable, secure, decentralised, and scalable blockchain.
The Merge also significantly impacts the dynamics of ETH the asset. A trifecta of factors will come into play upon Merge, which will change the market supply and demand pressures of ETH. Are these changes bullish or bearish? Only time will tell.
The Merge is finally coming and it’s coming soon.
To learn more about The Merge or to invest in ETH, speak to your personal broker today.
Recommended reading: What is Ethereum? A Beginner's Guide
Disclaimer: This assessment does not consider your personal circumstances, and should not be construed as financial, legal or investment advice. These thoughts are ours only and should only be taken as educational by the reader. Under no circumstances do we make recommendation or assurance towards the views expressed in the blog-post. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. The Company disclaims all duties and liabilities, including liability for negligence, for any loss or damage which is suffered or incurred by any person acting on any information provided.
from Caleb & Brown Cryptocurrency Brokerage.