Summary
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a payment protocol that operates on top of the Bitcoin blockchain. It’s designed to enable fast, cheap and secure off-chain transactions of Bitcoin for Lightning users.
The Lightning Network simultaneously addresses Bitcoin’s weaknesses and leverages its strengths, providing a platform to send and receive Bitcoin quickly with negligible fees.
These two characteristics promote Bitcoin’s adoption as a currency to use in all circumstances, from buying a coffee to exchanging hands in multi-billion dollar value transactions. As a result, many see the Lightning Network as pivotal in broadening Bitcion’s use case, allowing it to rival and potentially replace traditional payment systems, such as Visa and Mastercard.
What is the Lightning Network?
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a layer 2 solution that sits on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, a layer 1 protocol. Lightning doesn’t have a native token or blockchain; it utilises Bitcoin’s infrastructure – the asset Bitcoin itself and the blockchain – to create payment channels that facilitate the flow of Bitcoin from one party to another, away from the base bitcoin blockchain – in other words, off-chain.
Parties then can conduct multiple Bitcoin transactions, although each isn’t verified individually on the Bitcoin blockchain at the time of execution on Lightning's network. Instead, all the transactions in a payment channel are eventually reflected on-chain / on the Bitcoin network, as a single transaction.
In short, lots of transactions on the Lightning Network are rolled into one transaction on the Bitcoin network. Herein lies the Lightning Network’s power!
While the Lightning Network leans heavily on Bitcoin's infrastructure, it runs its own software that processes and logs all transactions on a standalone network of nodes (computers). These individual Lightning nodes communicate with one another to allow for the creation of the payment channels for Lightning users to move Bitcoin through.
How does the Lightning Network Work?
Lightning Payment Channels
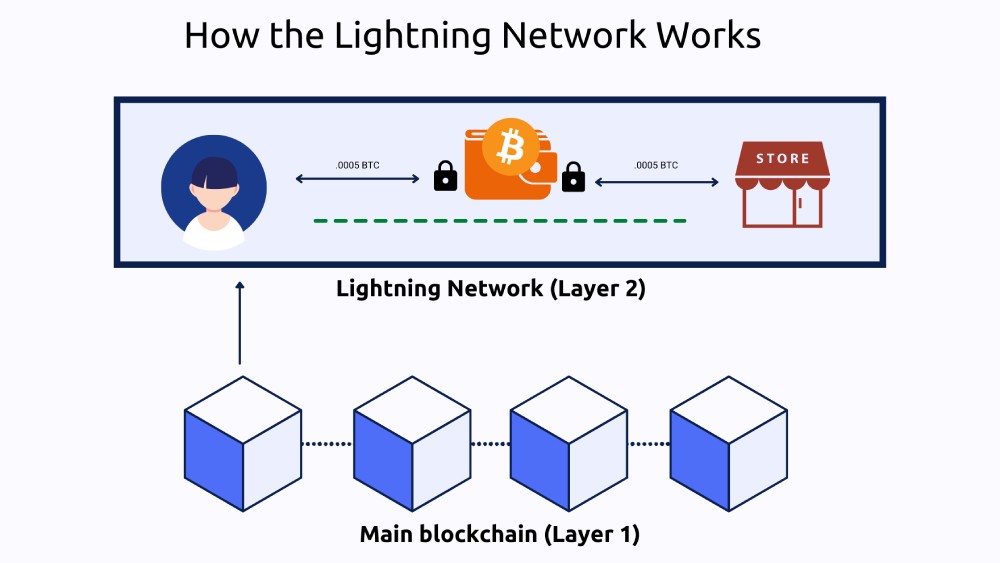
The Lightning Network works by creating payment channels between users. A payment channel is an agreement between two users to transact with each other, off-chain, to avoid the costs and delays of frequent on-chain (Bitcoin) transactions.
Here's how it works:
1. Channel creation: To create a payment channel, two users deposit an agreed upon amount of Bitcoin into a channel. This initial transaction creates a ledger on the Lightning network to log the following transactions between the two users, away from Bitcoin’s chain.
2. Off-chain transactions: Once the channel is created, the two users can transact with each other, at low cost. Each transaction is recorded in the ledger, which doubles as a balance sheet to keep track of the movement of funds. As long as the channel remains open, they can send unlimited transactions to each other.
3. Channel closure: The channel can be closed at any time by either party. When this happens, all transactions are calculated and consolidated into a single transaction that is posted to and finalised on the Bitcoin chain. At this point, the correct balances are credited to each user's respective wallet on the Bitcoin network.
The only Lightning-related transactions that are broadcast to the Bitcoin network are the opening and closing of channels.
For example: Let’s say you go to your local coffee shop every day and want to pay in Bitcoin. With Lightning, you could open up a payment channel with the coffee shop with funds locked into the channel. Each coffee purchase would be recorded within that channel, and the transaction would be instant and cheap. When the Bitcoin that started the channel is spent, you can choose to close the channel or refill it. If you choose to close it, all transactions within the payment channel will then be recorded on the main Bitcoin blockchain as one transaction.
Lightning Network Routing
Cleverly, the Lightning Network doesn’t need to create channels between each and every user. If multiple channels indirectly connect one use with another, payments can flow through them, similar to routing data on the internet. Routing allows transactions between unconnected parties to occur by transferring funds through interconnected pathways. This can work across multiple ‘hops’, meaning you can effectively pay anyone to whom a path exists. The nodes on Lightning naturally search for the best route to perform the transaction.
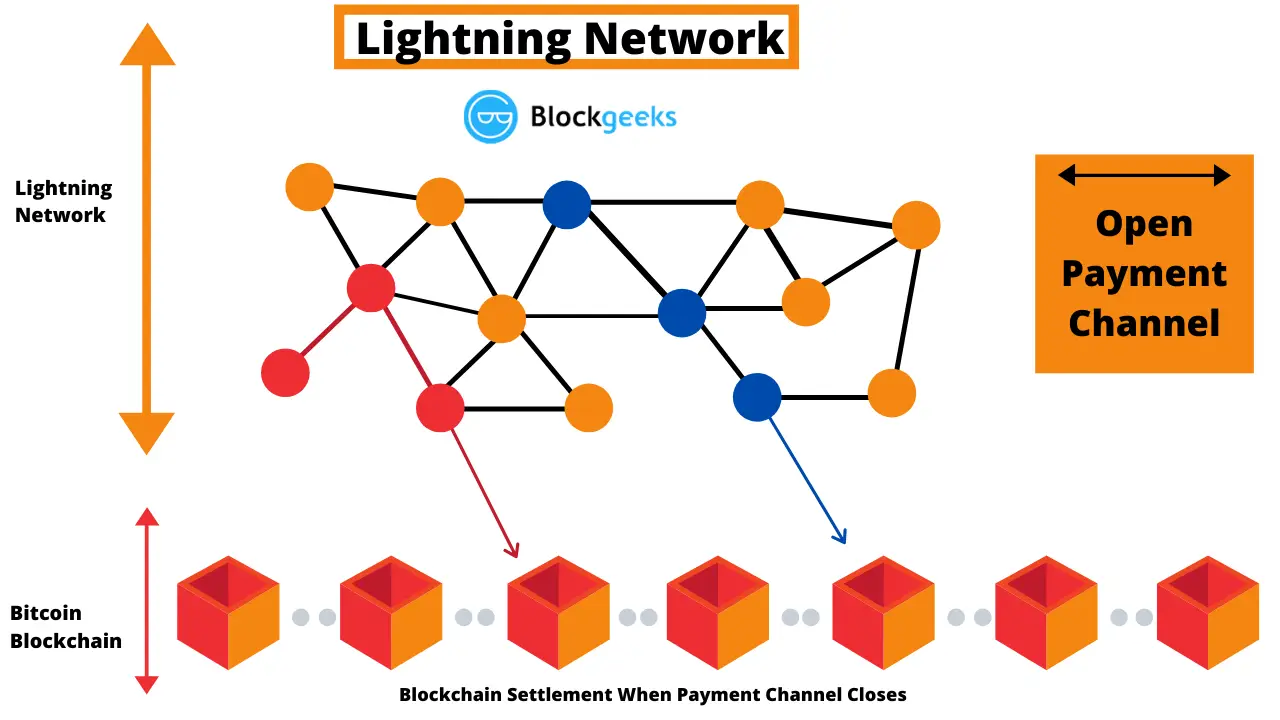
For example: If your friend (the orange dot one in from the left in the top row above), who you have a channel with, takes you (the far left orange dot) to their favourite coffee shop (the blue dot in the middle of the top row), which they have a channel with, Lightning would allow you to route your payment through your friend when you pay for coffee without needing to open a channel with the coffee shop.
Why is the Lightning Network Important?
Bitcoin remains the largest cryptocurrency in the world by market cap and has established a strong narrative as a store of value, which is why it’s been coined ‘digital gold’. However, Bitcoinfaces scaling challenges as it grows, with the limitations below preventing it from evolving into a day-to-day medium of exchange, like the US Dollar which changes hands with minimal friction around the world.
Transaction fees: Block space is a scarce resource (only 1 MB). Bitcoin blocks are created approximately every 10 minutes, and can only hold so many transactions. Transaction fees can fluctuate wildly based on network demand. For example, at the height of the 2017 bull market, fees exceeded $50.
Transactions per second: Bitcoin is only capable of approximately 7 transactions per second (TPS).
Network congestion: Slow block times and heightened use of the network can result in delays in transaction processing.
The Bitcoin Lightning Network was developed, in part, to encourage the use ofBitcoin for day-to-day payments, it to functionlike the peer-to-peer digital cash envisioned by Satoshi Nakamoto in the Bitcoin their white paper.
There are several benefits to using the Lightning Network, with some of the main ones discussed below.
What are the Benefits of the Lightning Network?
Instant Payments: True to the name, this protocol delivers lightning-fast payment transactions. Free of block confirmations to wait on, payments are processed as fast as your internet connection will permit.
Scalability: While the Bitcoin blockchain can typically handle 7 TPS, Lightning can handle millions of TPS, theoretically. This capacity dwarfs legacy payment systems – the Visa network typically processes around 1,700 TPS on average.
Low cost: By transacting and settling off-chain, Lightning allows for exceptionally low fees – generally fractions of a cent; transactions are also far less energy intensive given no mining is required to verify every transaction, so it’s greener too.
Privacy: Lightning offers users a high degree of confidentiality. Parties do not need to make their channels known to the broader network. Only the opening and closing of channels is recorded on-chain, so onlookers cannot view individual transactions within the channel.
A Lightning channel is a bidirectional payment channel, meaning both parties can send and receive payments across the channel. To create a payment channel, parties must deposit or lock some Bitcoin into the channel. Once open, a Lightning channel enables both parties to execute any number of transactions cheaply and instantly. The channel acts as its own mini-ledger, where users can transact between them without broadcasting every transaction to the base layer of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Current State of the Lightning Network
Since its launch in 2018, Lightning has seen impressive growth. As of February 2023, Lightning boasts upwards of 16,100 online nodes, 76,000 active channels and just over 5300 BTC in capacity. An amazing global visualisation of the Lightning Network and its node connections can be seen below.
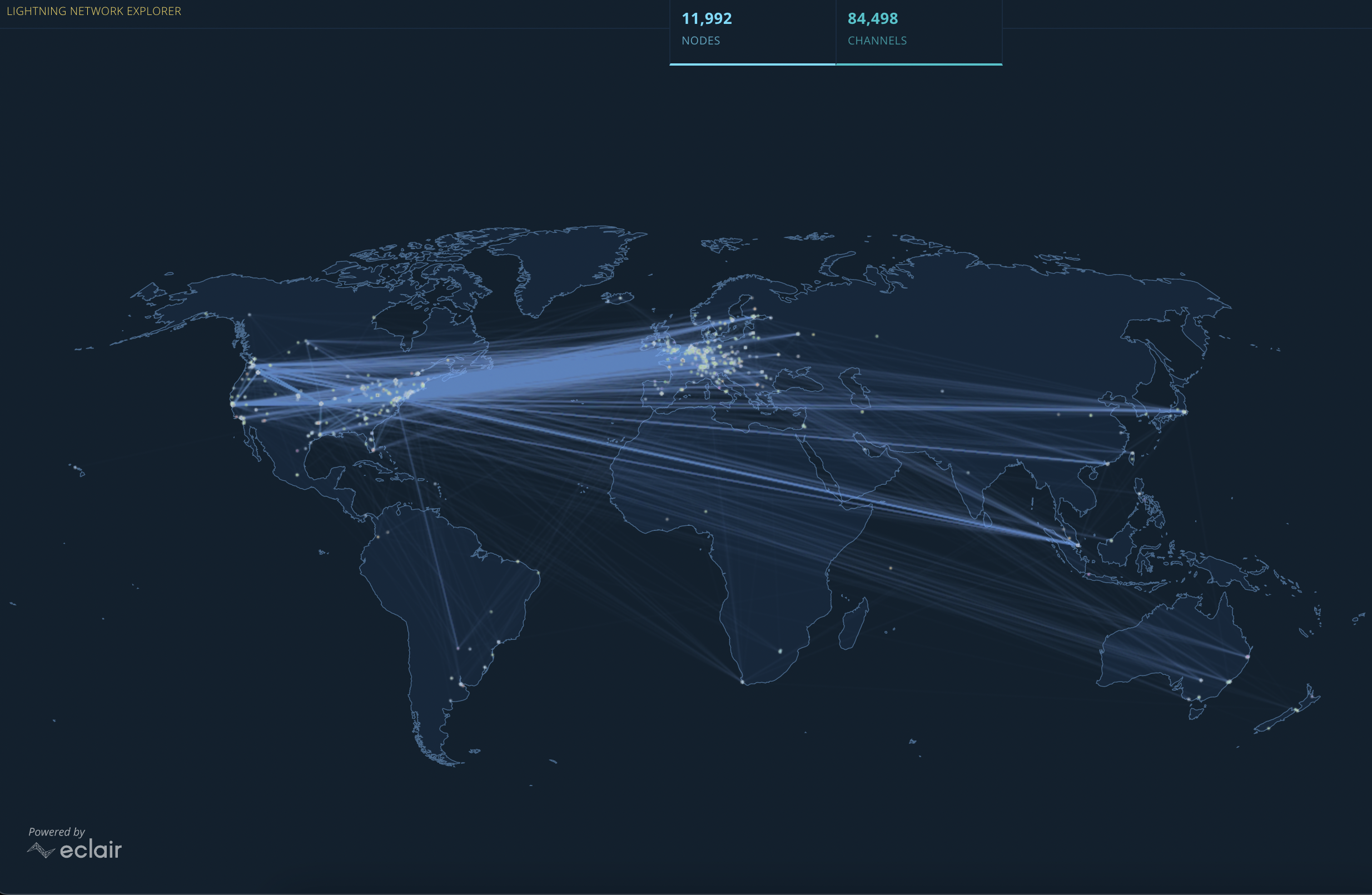
Since 2022, the network’s growth in terms of nodes and channels has plateaued according to Bitcoin Visuals. If more individuals, entrepreneurs and businesses seek to make and take payments in BTC, Lightning’s scaling technology will be key in democratising Bitcoin for mass adoption. Lightning offers emerging use cases to further this, including:
Cross-border remittance payments: After becoming the first nation to declare Bitcoin legal tender, El Salvador’s government created Chivo, a Lightning compatible wallet designed to enable seamless cross border payments. In the 45 days after launching, Chivo saw over 4 million users.
Micropayment streaming: Unlike the base layer Bitcoin Network, Lightning has no minimum transaction value. As a result, Lightning opens the frontier of micropayments. New digital business models have become possible for the first time, where websites or content creators can charge per article or per view of their site.
Social media tipping: Platforms like Twitter and Substack allow users to send and receive bitcoin ‘tips’ via the Lightning Network.
Future of the Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a crucial innovation in Bitcoin’s path to becoming a widely accepted medium of exchange, used on a day-to-day basis. As more people join the Lightning Network, the use cases for holding Bitcoin should rapidly expand and vice versa.
Though there are still some usability obstacles to overcome, as it currently requires some degree of technical proficiency to operate a Lightning node and wallet. With the amount of innovation taking place, it shouldn’t be long before we see considerable improvements to the user experience that will erode the barriers to entry.
Reporting on El Salvador’s Bitcoin experiment, the NBER (National Bureau of Economic Research) surveyed a sample of the population to measure Bitcoin usage. As of mid-2022, over 68% of citizens were aware of Chivo Wallet, but only 9.3% transacting with Bitcoin using the Lightning Network-compatible, national wallet.
With the above said, the success of the Lightning Network will almost certainly come down to Bitcoin’s mass adoption. Any technical hurdles would likely be overcome if the investment warranted it off the back of increased Bitcoin usage and demand.
Recommended reading: What is Bitcoin Halving?
Disclaimer: This assessment does not consider your personal circumstances, and should not be construed as financial, legal or investment advice. These thoughts are ours only and should only be taken as educational by the reader. Under no circumstances do we make recommendation or assurance towards the views expressed in the blog-post. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. The Company disclaims all duties and liabilities, including liability for negligence, for any loss or damage which is suffered or incurred by any person acting on any information provided.
from Caleb & Brown Cryptocurrency Brokerage.


.jpg?u=https%3A%2F%2Fimages.ctfassets.net%2F4ua9vnmkuhzj%2FuIaUbUNRbO1LdljRWKvoI%2Fd93965ff275cd47f8c19fcc71edcd42e%2FBitcoins_Market_Cycle_V3-01__1_.jpg&a=w%3D480%26h%3D270%26fm%3Djpg%26q%3D80&cd=2023-02-21T06%3A17%3A39.793Z)
.jpg?u=https%3A%2F%2Fimages.ctfassets.net%2F4ua9vnmkuhzj%2F7meVnT2vnQelBrt6W5yw73%2F8469fbdea8168e404fff363b35dd65a4%2FBitcoin_Halving-01__1_.jpg&a=w%3D480%26h%3D270%26fm%3Djpg%26q%3D80&cd=2023-01-10T02%3A22%3A06.649Z)


