- What is Cardano?
- How is Cardano different from Ethereum?
- How Does Cardano Work?
- What is ADA?
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Cardano
- Who Created Cardano?
- A Brief History of Cardano
- How to Invest in Cardano (ADA) in 2022
- How to Store ADA
- What's Next For Cardano?
- FAQs
- Invest in Cardano (ADA) with Caleb & Brown
Key Points
- Cardano was founded in 2017 by Charles Hoskinson, one of the co-founders of Ethereum.
- Cardano is the first crypto project founded on peer-reviewed research and developed through evidence-based methods.
- Using a multi-layered blockchain, where each layer performs a specific function, could make Cardano better equipped to scale over time.
- The roadmap for Cardano consists of 5 phases: Byron, Shelley, Goguen, Basho, and Voltaire. Each of these phases is named after a historical figure in academia, and ushers in a new set of features for the entire network.
What happens when you apply deep research, testing, and rigorous academic standards to cryptocurrency?
You get a network like Cardano.
Founded by an Ethereum co-founder who wanted to bring his own vision to life, Cardano fused crypto concepts with academic theory, prioritising a scientific method-like approach to building out a network.
In this guide, we uncover all that Cardano has to offer, a beginner breakdown of how the network operates, and show what’s next on the roadmap for this innovative crypto. Let’s dive in.
What is Cardano?
Cardano is a third-generation, open-source, proof of stake (PoS) blockchain built from the ground up by bright minds in both crypto and academia. Using a first principles approach combined with scientific research methods, Cardano has consistently held a position within the top 10 crypto by market cap since its launch.
Cardano differentiates itself from other blockchain projects by forming deep partnerships with leading academics and universities. In contrast to the ‘fail fast, pivot often’ modus operandi of the modern-day tech company, Cardano takes a more systematic approach. Code upgrades are held to strict mathematical standards and painstakingly reviewed before implementation. Rather than failing publicly, the network opts to perfect every process first, even if it takes longer than intended.
Outside of this, the Cardano network is home to hundreds of native assets and decentralised applications (DApps). Many of which, have become live over the past 12 months as the network has attracted more developers. Like Ethereum, these apps and assets are made available through the use of programmable smart contracts.
Recommended reading: What is a Layer 1 Blockchain?
How is Cardano different from Ethereum?
While the Ethereum and Cardano networks share some similarities—including a co-founder—both blockchains are quite different.
Cardano, a third-generation blockchain, seeks to build upon the capabilities of Ethereum 1.0. This includes using an energy-efficient PoS consensus model, and multiple layers for future blockchain scalability.
On September 15, 2022, Ethereum’s long-awaited Merge was executed, marking the network’s transition from a Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
Outside of this, the essential difference between Cardano and Ethereum is formal verification. Although both networks can be used for global transactions and executing smart contracts, Cardano is the first formally verified—and therefore provably secure—network.
How Does Cardano Work?
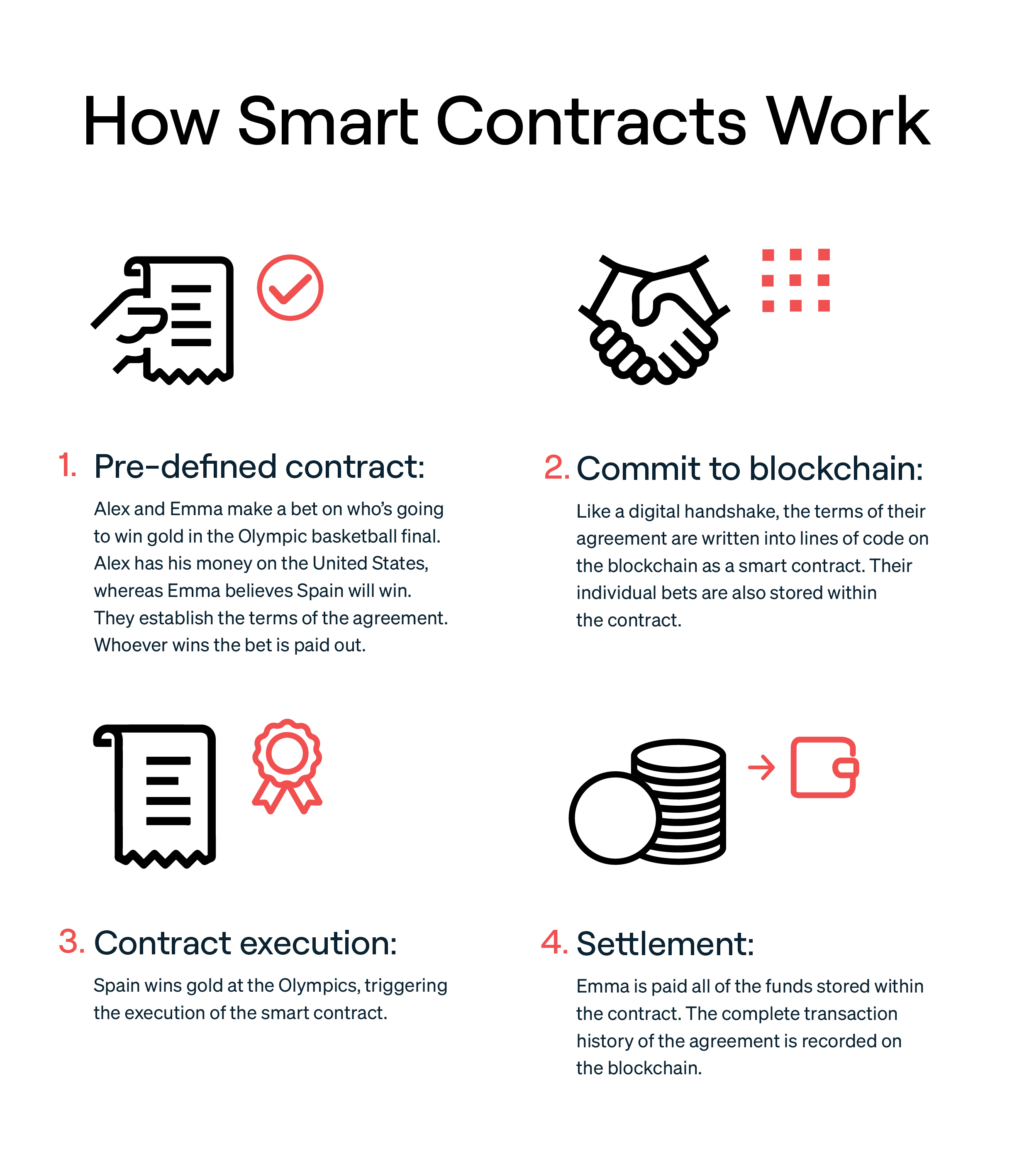
Smart Contracts
Similar to regular contracts in the real world, smart contracts have a set of conditions and rules. These are written digitally in one of Cardano's programming languages, Plutus or Marlowe (both of which are powered by Haskell).
Rather than relying on an intermediary (e.g. lawyer) to ensure all contract conditions are met, smart contracts simplify trade between parties, auto-executing the terms of an agreement without the need for a third party.
The use of smart contracts on the Cardano blockchain gives the network significantly more utility, while reducing the overall cost to create and implement contracts between two parties.
Multilayered Blockchain
Cardano has multiple layers which serve different purposes. The base layer is the Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL), where users can transact with each other using ADA. The second layer is the Cardano Computational Layer (CCL), responsible for executing smart contracts and verifying security through the use of various protocols. Both layers are programmable, opening up the potential for Cardano to handle the challenges of scaling in the future.
The Ouroboros Protocol
Cardano uses a PoS consensus mechanism (known as Ouroboros) to validate transactions on the network. Similar to other PoS consensus models, users can stake their crypto in exchange for potential rewards. Here’s how it works:
- A user who has staked ADA—and operates a validator node—is randomly assigned the role of slot leader. They are responsible for validating a block of transactions within a certain time slot (known as an epoch).
- The more ADA you have staked, the higher probability of selection.
- Slot leaders with enough computational power and technical know-how can choose to validate their own epoch; keeping the reward for themselves.
- Alternatively, they can partition the epoch to other validators and split the rewards.
Anyone who has ADA stored in a Cardano native wallet can also delegate their stake to a stake pool operator to carry out the validation process on their behalf.
Stake pool operators are charged 340 ADA by the network for every successful block validation. This fee is split among the operator and other investors within the stake pool. Operators will also charge a fee to investors using the pool for staking.
Decentralised Apps (DApps)
Smart contracts also have paved the way for the creation and use of DApps. Like smartphone or computer applications, DApps have a wide range of functionalities. Rather than running on a central server, the code of a DApp is committed via a smart contract to the blockchain. Cardano’s peer-to-peer network can then execute the app’s smart contract without the need for a centralised authority.
NFTs
Within the last year, the network has added functionality for creating, collecting, and selling non-fungible tokens (NFTs). As Cardano NFTs are fairly new, time will tell whether their popularity exceeds the likes of earlier blockchains like Ethereum and Solana.
Tokenisation
Cardano also functions as a foundational layer (known as a Layer 1) for other crypto projects. Unlike Ethereum, these tokens are not created via smart contracts. Rather, they use the same architecture as ADA itself. Removing this step in the tokenisation process would theoretically reduce the fees associated with transactions. It could also boost security across Cardano, as hackers would need to penetrate the structure of the network itself, not a smart contract. For a more in depth comparison of Cardano native and ERC-20 tokens, we recommend reading this table.
Recommended reading: What is Proof of Stake in Crypto?
What is ADA?
ADA is the native crypto on the Cardano network, named after the 19th-century mathematician and world’s first computer programmer, Ada Lovelace. The network is also named after another famous mathematician, Geralamo Cardano. The two names are sometimes used synonymously, but ADA is the actual digital currency that powers the Cardano network.
Independent projects and assets run on the Cardano network. These projects need to continue using ADA to build, secure and scale their applications. This native token is also a finite resource, with its supply fixed at 45 billion ADA. Its limited supply works to ensure the token remains valuable as long as there is user demand for the network and its potential use cases. ADA is vital for propelling economic activity on Cardano.
Outside of this, ADA is distributed as a reward for validating transactions, used as payment in the buying and selling of NFTs, and the use of DApps.
ADA is stored in Cardano-based wallets, Daedalus and Yoroi; the latter being a beginner-friendly, light option for investors. In the future, ADA will also be used as a governance token, which will allow holders to vote on changes and upgrades to the Cardano platform.
Recommended reading: 6 Types of Altcoins & Their Uses
Advantages & Disadvantages of Cardano
Cardano has taken a “slow-and-steady” approach towards innovation, testing the system countless times before releasing any new updates. This approach is one of the reasons why Cardano is one of the more unique projects in the market today.
While the project is shaping up to be a leading smart contract platform, there is still room for improvement. Let’s explore what sets Cardano apart from other blockchain networks, as well as some challenges that the network is trying to overcome.
Advantages
- Security: Ouroboros, Cardano’s blockchain protocol, uses an environmentally-friendly PoS consensus mechanism (as opposed to Proof of Work) to uphold network security. Ouroboros is also the first peer-reviewed, tested, and formally verified protocol in crypto. Combining methodologies from cryptography and other scientific disciplines, the developers of Cardano have made a completely trustless network, impenetrable by hackers so far. Two anonymous parties can complete a transaction without an intermediary, knowing that the financial network is backed by rigorous, ongoing testing.
- Decentralised: Decentralisation ensures that governance is distributed across the network. No one individual, organisation, or even government can take control of the network and use it to their advantage. Cardano is open-source, distributing data—and essentially trust—to all its users. Because of this, there is no need for a centralised authority to manage the network and mediate transactions.
- Programmability: Cardano's highly programmable networks allows newly developed DApps to interact with already existing protocols on the network. Like lego blocks, any smart contract, app, or protocol built on the network can interact or integrate with each other, leading to even more creative uses for Cardano.
- Tokenisation: Any item that can be registered in a digital format can be tokenised on Cardano. While tokenisation is commonly used in the NFT space, it has real-world applications in real estate, art, and even gold. Think of it as a digital certificate of ownership for an asset.
- Developer Activity: In the lead-up to Cardano’s Vasil Upgrade, developer activity has increased on the network. High development activity is often correlated with an overall belief in the network’s utility and public sentiment that the project could achieve the goals it is aiming for.
- Scalability Potential: Cardano was built with future scalability in mind. This is one of the reasons why it uses PoS, and allows developers to create new native tokens without the need for smart contracts. Although the network has yet to handle the volume of the likes of Ethereum or Bitcoin, its internal structure is built to effectively manage large growth over time.
- Historical Performance: Since its launch, ADA has ranked within the top 10 cryptocurrencies by market cap. Its ability to remain in this position is a testament to the utility of the Cardano network and its strong community of holders. Understand that past performance is in no way an indicator of future results, and market cap is just one of many factors that speak to the potential value of a project. Saying this, ADA’s ability to endure market swings is a feature that suggests it isn’t going away anytime soon.
Disadvantages
- New Project: Compared to Bitcoin and Ethereum, Cardano is a relatively new project. While it has had much success and consistently ranks among the top crypto by market cap, the project will have to continue to innovate and find more utility and adoption in order to scale.
- Unfamiliar Programming Language: Although Cardano’s programming language, Haskell, is one of the most popular languages for developers to learn, it has not been widely adopted since its release in 1990. Developers seeking to create applications on Cardano’s blockchain might need to spend additional time learning Haskell first. .
- Move Slow, Build Slow: Although Cardano is taking an innovative approach to crypto, it is not the first project to enter the market with similar qualities. In addition to this, the founders have chosen to take a slow methodical approach to build out network features. This approach could help the network avoid bugs and potential hacks. In turn, it also gives other projects who choose to move quickly more opportunities to catch up with Cardano.
Who Created Cardano?
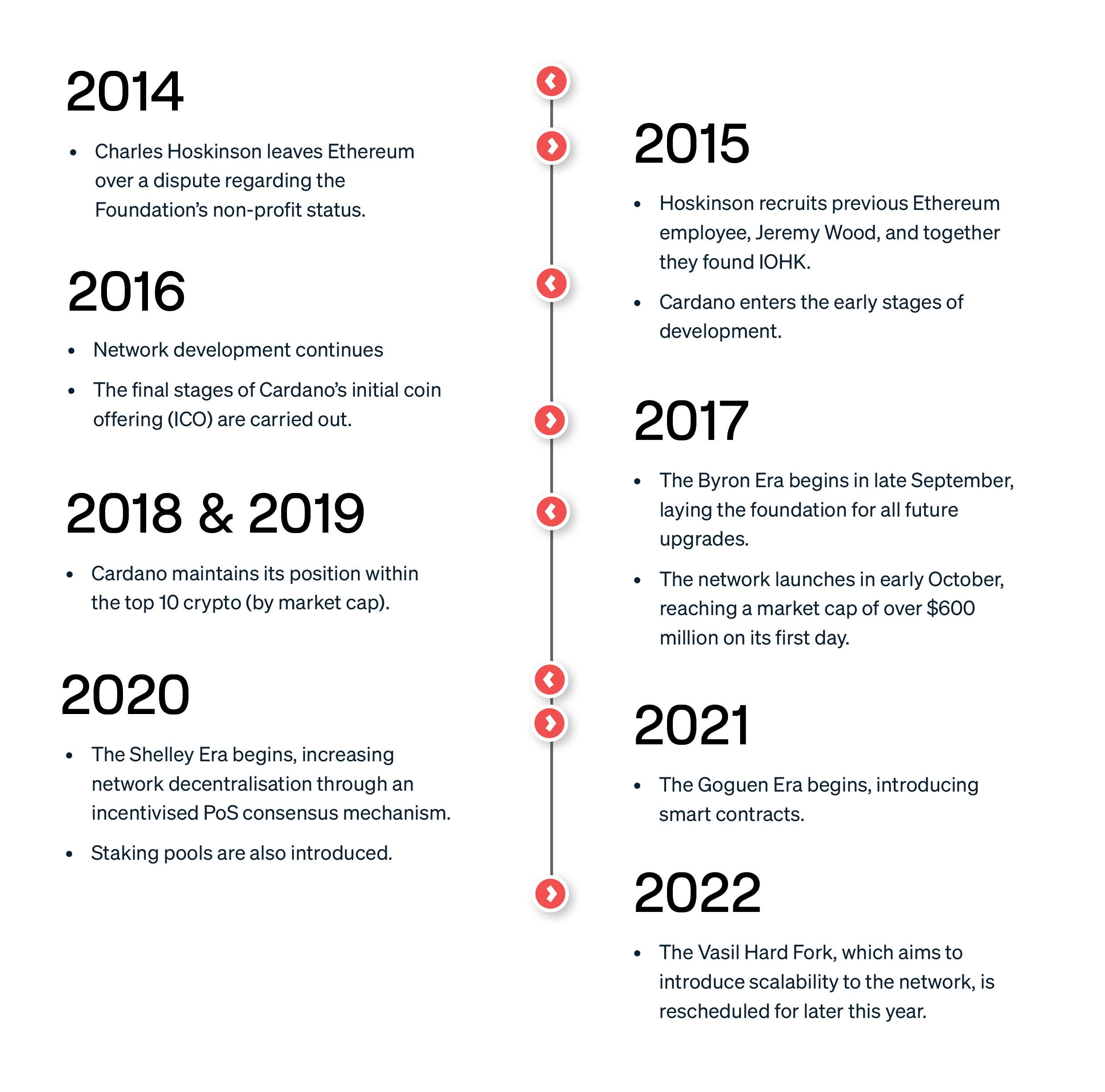
In 2013, Charles Hoskinson left his job in consulting to create the Bitcoin Education Project. Through this online school, he met Vitalik Buterin, and they eventually joined forces (along with a few others) to create Ethereum.
Towards his later days with the Ethereum Foundation, Hoskinson was in the process of developing a for-profit blockchain model. Hoskinson strongly believed in his concept, whereas Buterin wanted Ethereum to maintain its non-profit status. Unable to reconcile their differing opinions, Hoskinson split from the organisation entirely. He recruited Ethereum Foundation employee Jeremy Wood and began to work on Cardano exclusively.
Development on Cardano began in 2015 through Hoskinson and Wood’s newly founded company: Input Output Hong Kong (IOHK). The network became available to the public in 2017.
A Brief History of Cardano
How to Invest in Cardano (ADA) in 2022
Buying ADA
There are three primary ways to obtain ADA - buying, earning, or staking. While staking is relatively affordable on Cardano, investors who do not have a validator node set up will have to delegate their stake to an existing validator. If you prefer to have more control over your investment, consider buying ADA outright.
The easiest way to buy ADA is through a brokerage like Caleb & Brown. If you’re ready to dive in and make your first ADA purchase, Caleb & Brown is here to help. Trusted by over 22,000 investors across 100 countries, our dedicated team of experts works around the clock to carry out all your ADA trades.
Recommended reading: How to Buy Cardano (ADA) in 4 Simple Steps
Selling ADA
Selling your ADA with Caleb & Brown is as simple as buying. You can trade your ADA for any of the 100s of assets available through our brokerage.
Should you decide to exchange your ADA for fiat currency, there are $0 withdrawal fees as well.
How to Store ADA
There are multiple ways of storing ADA, from a cold wallet, hot wallet or with a custodian. Individual risk tolerance and preferences will determine the method employed by most users.
Cold wallets are completely disconnected from the internet. As such, they cannot be easily hacked and are often seen as a safer option for infrequent traders. These storage devices often resemble USB flash drives. Cold wallets have additional built-in layers of security to prevent a data breach once you connect it to the internet for trading.
Hot wallets are connected directly to the internet, usually through a phone or desktop application. Their popularity lies in their ease of use and ability to make trades quickly.
Many of these storage methods can seem complex, especially if you are not tech-savvy. Caleb & Brown provides end-to-end custody solutions for hassle-free storage and peace of mind investing. We have a battle-tested security infrastructure, through the leading asset security platform Fireblocks. All clients receive a free security consultation to ensure they follow security best practices.
Recommended reading: Crypto Security Part 1: Best Practices
What's Next For Cardano?
The Cardano network is currently in its third of five phases on its roadmap. Goguen (the current era of Cardano) introduced smart contracts to its ecosystem.
The fourth phase, Basho, will focus on developments that improve blockchain performance. The goal of this era is to create optimisations that increase the scalability and interoperability (the ability of multiple chains to share information laterally) of the entire network.
The fifth and final phase is Voltaire. This era will introduce self-sustainability through treasury and voting systems. ADA will also function as a governance token, allowing network participants to decide the future direction of the project.
FAQs
Is Cardano a good investment?
Choosing to buy ADA depends largely on your investment goals. Investors also weigh a variety of factors before choosing a project to invest in. Ultimately, it’s up to you to determine whether you decide to invest in SOL, and what strategies you use to maintain that investment.
At Caleb & Brown, we follow the facts; not opinions or trends. We encourage you to do your own independent research before making an investment. Our team of crypto experts are more than willing to answer any questions you have along the way.
Why does ADA have value?
Like any other asset, ADA’s value is determined by markets. It’s globally accessible, and people will readily buy ADA with other forms of money (e.g. dollars, euros, Bitcoin, etc.). People will use ADA as digital money to pay for goods and services, such as NFTs, DApps, or other coins. Knowing this, ADA has value because users will readily exchange it for other things considered valuable.
Yet understanding why ADA is at a certain price point is a more complex topic to unravel. It’s a delicate mix of investor belief in the value that the Cardano project creates, along with some fundamental principles that should be met for an asset to be considered valuable.
For further insight into the value of crypto, we recommend reading our Why is Bitcoin Valuable explainer.
When did the Vasil Hard Fork go live?
In September 2022, Cardano completed the Vasil hard fork upgrade. This was designed to improve scalability and clear the way for the development of decentralised applications (dApps).
How many transactions can Cardano do per second?
Currently, Cardano can handle up to 250 transactions per second (TPS). It aims to exceed 1 million TPS in the coming Hydra update.
What consensus mechanism does Cardano use?
Cardano currently uses a Proof of Stake consensus mechanism.
Invest in Cardano (ADA) with Caleb & Brown
Investing in crypto doesn't have to be complicated.
Caleb & Brown is the world's leading cryptocurrency brokerage for those looking to invest in ADA or other digital assets.
Our personalised broker service makes crypto investing simple. A dedicated member of our broker team is always on hand to guide you along the way, giving you the confidence you need to navigate the world of crypto. Not to mention key features such as:
- No joining or signup costs
- Industry-leading storage solutions
- 24/7 customer support
If you are ready to take the next step and invest in ADA, contact your crypto broker today.
Not yet a client? Sign up for your free consultation.
Recommended reading: How to Buy Cardano (ADA) in 4 Simple Steps
Disclaimer: This assessment does not consider your personal circumstances, and should not be construed as financial, legal or investment advice. These thoughts are ours only and should only be taken as educational by the reader. Under no circumstances do we make recommendation or assurance towards the views expressed in the blog-post. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. The Company disclaims all duties and liabilities, including liability for negligence, for any loss or damage which is suffered or incurred by any person acting on any information provided.
from Caleb & Brown Cryptocurrency Brokerage.




.png?u=https%3A%2F%2Fimages.ctfassets.net%2F4ua9vnmkuhzj%2F1PjLgWLIMUO2pzaZiPx5Dh%2F3348eab4e3ed605ef2edb43ec8e1f74f%2FBlog-Cover__15_.png&a=w%3D480%26h%3D270%26fm%3Dpng%26q%3D80&cd=2023-02-28T02%3A58%3A44.085Z)

