Key Points
- Polygon was founded in 2017 by Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun, and Mihailo Bjelic.
- Formerly known as the Matic Network, it prioritises creating interoperable scaling solutions for Ethereum-compatible blockchains.
- Developers have been drawn to create on Polygon due to its low fees and compatibility with Ethereum.
- Polygon’s goal is to make Ethereum accessible to everyone, by creating a secure multi-chain network that is compatible with—and scales with—Ethereum.
Polygon brings the world to Ethereum. Optimised for speed, it’s a network of interconnected blockchains that all lead back to Ethereum’s mainnet.
Founded in 2017, Polygon drew attention as an Ethereum blockchain problem-solver; creating unique solutions to help the network grow and scale over time.
But what has Polygon become today, and what’s in store for its future?
Let’s explore the key features of Polygon, its native token, MATIC, and how the network seeks to differentiate itself from other layer 2 blockchains.
What is Polygon?
Founded originally as the Matic Network before undergoing a rebrand, Polygon is a layer 2 solution designed to improve the scalability and efficiency of Ethereum.
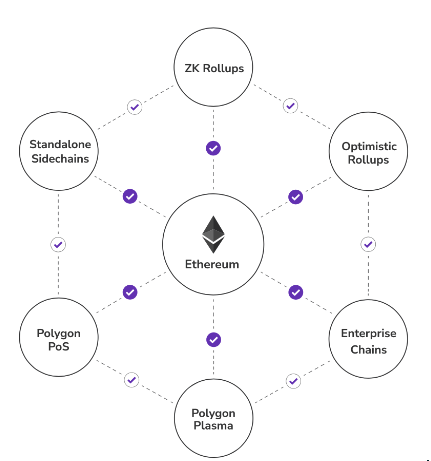
Like the shape from which it gets its namesake, there are many sides to this project. Not limited to one blockchain, Polygon uses a multi-chain system that allows users to seamlessly enter the Ethereum network of decentralised apps (DApps) and digital assets. Polygon is also home to many of its own DApps, which are compatible with Ethereum as well. Outside of this, the network serves as a bridge between Ethereum and other Ethereum-compatible blockchains.
The ultimate goal of the project is to create an interconnected network of blockchains to overcome the limitations of one single chain.
Affordability, scalability, and security are the key limiting factors it seeks to solve.
Recommended reading: What is a Layer 2 Blockchain?
What is MATIC?
MATIC is an ERC-20 token and Polygon’s native utility token; a coin that provides a service to a network. MATIC serves the Polygon network in a variety of ways.
It functions as a governance token when users want to propose and vote on changes within the network.
It maintains network security through staking and is given as a reward to users who participate in the process (either as a validator or delegator).
And any transaction fees incurred through network use are charged and paid for by users in MATIC. These are often referred to as ‘gas fees’.
The total MATIC supply is capped at 10 billion. At the time of this writing, 87% of the total supply (8.7 billion) is circulating in the market.
How Does Polygon Work?
Ethereum is the local line. Polygon is the express train.
While both trains are making the same journey, Ethereum stops at every station along the way, carrying a limited number of passengers along for the ride.
Polygon runs alongside Ethereum’s route but only stops at major destinations; picking up large groups of passengers and transporting them to the next major destination along the way.
How does Polygon do this? Rather than relying on one solution, it uses multiple technologies to transport information as efficiently as possible. These solutions are known collectively as sidechains, as they run independently and parallel to the Ethereum network.
Proof of Stake
Polygon’s primary chain uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism and is known as Polygon PoS. This is an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible sidechain that is secured by a permissionless group of validators. Validators are rewarded in MATIC when they stake their own MATIC and successfully validate transactions on the network.
Delegators can also participate in staking by delegating their stake to a validator.
Recommended reading: What is Proof of Stake in Crypto?
Polygon Bridge
So how does Polygon actually connect to the main Ethereum network? There are two ways, and together they are known as the Polygon Bridge.
Polygon PoS
This is the PoS Chain that users can use to transfer assets between Ethereum and Polygon. It is relatively faster, and uses the same consensus mechanism as Ethereum. This chain is ideal for users making frequent transactions, or only moving relatively small amounts of crypto at a time.
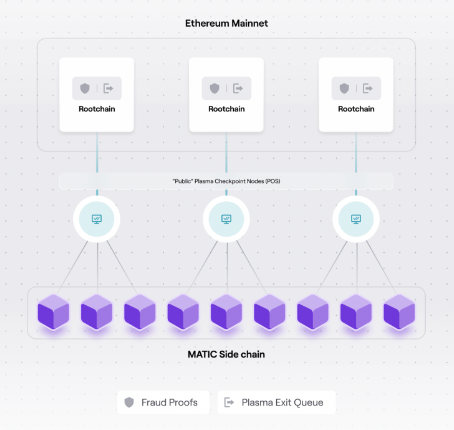
Plasma Chain
This chain is a framework of Ethereum child chains, basically smaller copies of Ethereum. It validates transactions off-chain, and bundles these transactions before transmitting that data to Ethereum.
Since validation is completed off-chain, there are additional stopgaps and security layers to ensure the transaction data isn’t falsified. Because of these additional security measures, plasma chain transaction times are relatively longer than Polygon PoS times. There is a 7-day withdrawal period for all exits and withdrawals from Polygon to Ethereum on the Plasma Bridge. For time-sensitive transactions, the significantly faster Polygon PoS is ideal.
The Plasma Chain tends to be used more by DApp developers who may perform less frequent—but larger—transactions at a given time.
Zero-Knowledge Rollups
Another way Polygon attempts to unclog traffic in and out of Ethereum is through zero-knowledge rollups (ZK-rollups). This scaling solution increases throughput on the Ethereum Mainnet by bundling thousands of transactions into one single transaction. This data point is then presented to the Mainnet as a summary of all the transactions within the rollup.
Posting only the most essential transaction information reduces the amount of data that needs to be written onto the Mainnet, and should theoretically reduce overall transaction times.
Since these transactions are verified off-chain, Polygon ZK-rollups also produce validity proofs which cryptographically confirm that everything contained within the rollup is verifiably true
Optimistic Rollups
Like the name entails, optimistic rollups do not question the validity of transactions in any given rollup. Instead, these bundles of transactions are submitted without any cryptographic proof, working under the assumption that all the transactions should be true. During this submission period, optimistic rollups allow any user to challenge the authenticity of the transaction batch.
Where ZK-rollups execute a security protocol before submitting transactions to Ethereum. Optimistic rollups incentivise validators to participate in securing the network through the submission of fraud proofs. It also discourages dishonest validators from submitting fake fraud proofs as well.
Polygon Nightfall is the network’s most recent foray into rollups. This scaling solution—targeted at enterprises—uses a hybrid Optimistic-ZK rollup to record and validate transactions.
How is Polygon Different From Ethereum?
Polygon and Ethereum were formed from two different ideas. Ethereum founder, Vitalik Buterin seeks to create a secure, scalable network that does not compromise its decentralisation. Polygon founders seek to be the premier scaling platform for Ethereum. With two differing goals arises two networks that are structurally unique.
When Ethereum was a Proof of Work (PoW) network with remarkably high traffic, it encountered various issues that impeded its growth and usability. Transaction speeds were particularly slow during busy times. Gas fees would often skyrocket during these periods, which made it remarkably expensive for the average investor to participate in the network.
Polygon sought to solve these problems through the use of multiple sidechains, a PoS consensus model, and rollups. Ethereum decided to take their chances at solving these problems internally, gradually rolling out updates across the network.
While there is some overlap in how both networks attempt to solve the scalability trilemma, Ethereum will always be a standalone project. Polygon can only maintain its utility as long as people remain interested in using Ethereum.
In saying this, the two networks equally benefit from a synergetic relationship. Polygon and Ethereum work alongside one another, with both their future success reliant on the continued success of the other.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Polygon
Polygon has made significant strides in complementing and improving the Ethereum network. Yet no project is completely perfect. Let’s unravel what makes Polygon unique, as well as the obstacles it has faced along the way.
Advantages
- Low Fees: Through using PoS and rollups, transaction fees on Polygon are comparatively lower than other networks, like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
- Fast Transaction Times: Polygon gives users multiple options to move digital assets across the network. Rollups can bundle thousands of transactions into one succinct package. The PoS protocol is a relatively faster way to validate transactions (when compared to methods like PoW). This combination of scaling solutions leads to overall faster transaction times on the network.
- Designed to Scale: Polygon was designed from the ground up to scale and improve upon Ethereum. Each sidechain performs a unique function. Developers are not tied to building on any one particular chain. Users can transact on whatever chain they please. Polygon is not reliant on a one-size-fits-all solution for growth, allowing users to experiment and choose which solution works best for their needs.
- Staking: Users can also earn rewards by participating in securing the network. Validators are the more active participants, taking part in the consensus group work. Delegators typically take a more passive approach to staking by delegating their stake to a validator for a fee.
Anyone on Polygon can set up a node and become a validator for as little as 1 MATIC. It’s worth noting that auctions for validator slots are held regularly, indicating that most validators will probably be staking much more than the minimum.
- Vast Ecosystem: While Ethereum still operated as a PoW, developers flocked to Polygon for its low fees, ease of use, and interoperability. Since then, the network has become a home for over 37,000 DApps.
On top of this, Polygon users are not limited to what’s available on the network. They also have direct access to Ethereum’s suite of decentralised finance (DeFi), DApps, NFTs, and other digital assets. Polygon can also connect with other Ethereum sidechains, unlocking an even wider ecosystem. In this way, Polygon acts as a hub that connects Ethereum to the rest of Web3.
- Eco-Friendly: The project is currently carbon neutral. It has plans to go carbon negative in the latter part of 2022, and climate positive beyond that.
Disadvantages
- Not Autonomous: Some investors could be turned off by Polygon’s deep connection to Ethereum. It appears the network's utility relies almost entirely on Ethereum's continued growth. While Ethereum is one of the largest crypto networks in existence, if it fails, then it’s highly likely that Polygon will also fail.
- Limited MATIC Use Cases: Within the network, MATIC functions as a utility token. Yet its utility ends anywhere outside of Polygon. It’s also an ERC-20 token, which exclusively limits its use cases to Ethereum and other related networks.
- Slow Withdrawal Times: While the PoS Chain is fairly efficient, Polygon’s Plasma Chain has slow withdrawal times built into its design. Given the additional security measures used here, it may take users exiting Ethereum up to a week to transfer assets to Polygon. The PoS Chain is a faster alternative.
Who Created Polygon?
Seeking to create a network that complemented and improved Ethereum, the Matic Network was founded in 2017 by Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun, and Mihailo Bjelic.
While Anurag Arjun was the only founder without a programming background, the rest of the founders played key roles in developing and rolling out new Ethereum features. They understood what the network excelled at, as well as its pain points. They were perfectly positioned to create a layer 2 that could scale Ethereum.
In April 2019, the team held an initial exchange offering (IEO) on Binance. During this month, they sold 1.9 billion MATIC tokens raising the equivalent of $5.6 million in Ether.
The Matic Network went completely live in 2020 and has continued to gather a growing number of well-known proponents ever since. In early 2021, the project rebranded to its current name Polygon. Not long after, Mark Cuban invested in the project, and Polygon’s market cap exceeded $10 billion for the first time.
The Simple Way to Buy, Sell and Store MATIC in 2022
Buying MATIC
The easiest way to buy MATIC is through a brokerage like Caleb & Brown. We make purchasing MATIC easy and accessible whether you use fiat currency or crypto. Trusted by over 21,000 investors across 100 countries, our dedicated team of experts works around the clock to carry out all your crypto trades. If you’re ready to dive in and make your first MATIC purchase, open an account with us for free today.
Recommended reading: Common Crypto Investing Strategies Every Investor Should Know
Selling MATIC
Selling your MATIC with Caleb & Brown is as simple as buying. You can sell or swap your MATIC for any of the 100s of assets available through our brokerage.
Should you decide to exchange your MATIC for fiat currency, there are $0 withdrawal fees as well.
How to Store MATIC
There are multiple ways of storing MATIC, from a cold wallet, hot wallet or with a custodian. Individual risk tolerance and preferences will determine the method employed by most users.
Many of these storage methods can seem complex, especially if you are not tech-savvy. Caleb & Brown provides end-to-end custody solutions for hassle-free storage and peace of mind investing. We have a battle-tested security infrastructure, through the leading asset security platform Fireblocks. All clients receive a free security consultation to ensure they follow security best practices.
Recommended reading: Crypto Security Part 1: Best Practices
What’s Next For Polygon?
Polygon has gained and maintained relevance because it continues to iterate and discover novel scaling solutions for Ethereum developers and users. While the project has a long list of solutions currently in development, its most recent release is Polygon ID, a blockchain-native identity system. Using zero-knowledge technology, this service allows users to safely and securely verify their identity on chain, without any exchange of information between a third party.
Currently in the Mainnet Beta testing stage, is Polygon Nightfall, a hybrid Optimistic-ZK rollup that hopes to enable efficient, affordable, and decentralised business transactions.
FAQs
Why do Polygon and MATIC have value?
Polygon exists to solve problems affecting Ethereum’s future scalability. Proponents who support layer 2 solutions as a way to improve Ethereum will continue to find value in MATIC and its use cases on Polygon. The project also has a vested interest in Ethereum’s growth, becoming more valuable as more users adopt Ethereum.
How is Polygon different from Polkadot?
Both networks share the very similar goal of creating seamless connections between multiple isolated blockchains. Polygon has targeted its efforts towards the market-dominant Ethereum, and creating connections to make Ethereum more accessible across Web3. Polkadot on the other hand is not targeting any particular blockchain and is looking to establish connections between every major project on the market.
How many DApps have been built on Polygon?
Over 37,000 DApps have been launched and/or used on the network since the introduction of smart contract functionality.
What consensus mechanism does Polygon use?
The network uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism on its Mainnet.
Invest in MATIC With Caleb & Brown
Investing in MATIC doesn't have to be complicated.
Caleb & Brown is the world's leading cryptocurrency brokerage for those looking to invest in MATIC or other digital assets.
Our personalised broker service makes crypto investing simple. A dedicated member of our broker team is always on hand to guide you along the way, giving you the confidence you need to navigate the world of crypto. Not to mention key features such as:
- No joining or signup costs
- Industry-leading storage solutions
- 24/7 customer support
If you are ready to take the next step and invest in MATIC, contact your crypto broker today.
Not yet a client? Sign up for your free consultation.
Disclaimer: This assessment does not consider your personal circumstances, and should not be construed as financial, legal or investment advice. These thoughts are ours only and should only be taken as educational by the reader. Under no circumstances do we make recommendation or assurance towards the views expressed in the blog-post. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results. The Company disclaims all duties and liabilities, including liability for negligence, for any loss or damage which is suffered or incurred by any person acting on any information provided.
from Caleb & Brown Cryptocurrency Brokerage.




.png?u=https%3A%2F%2Fimages.ctfassets.net%2F4ua9vnmkuhzj%2F1PjLgWLIMUO2pzaZiPx5Dh%2F3348eab4e3ed605ef2edb43ec8e1f74f%2FBlog-Cover__15_.png&a=w%3D480%26h%3D270%26fm%3Dpng%26q%3D80&cd=2023-02-28T02%3A58%3A44.085Z)

